Click image for an enlarged view and more information.
 |
|
 |
C6.1. A field of genetically uniform daffodils. Gardeners prefer uniform flowers, but these plants are all equally susceptible to potential pathogens.
|
|
C6.2. Potato leaf from a susceptible plant (far right) and leaves from plants with varying levels of general resistance. General resistance functions against all races of the late blight pathogen, Phytophthora infestans. In resistant plants, lesions are smaller, develop more slowly, and produce fewer sporangia.. |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
| C6.3. Pepper plants developed through traditional breeding with resistance (Right) to bacterial leaf spot disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. vesicatoria) compared to susceptible plants (Left). |
|
C6.4. Genetically transformed tobacco plant that received the luciferase gene responsible for the luminescence of fireflies. The photograph was taken over a 24-hour period. Genetic engineering works because of the universal genetic code that allows an insect gene to function in a plant. |
|
|
|
 |
|
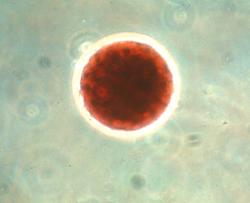 |
| C6.5. Transgenic tomato plants are resistant to Tobacco mosaic virus. The plants on the left have been transformed using the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. The coat protein gene of the virus was transferred to the DNA in the nucleus of the plant cell. Virus-resistant plants were regenerated from the transformed cells. Both sets of plants were inoculated with the virus, but only the plants on the right became diseased. |
|
C6.6. Cucumber protoplast stained with neutral red. The cell wall has been removed enzymatically, leaving only the cell membrane (light mircrograph).
|
| |
|
|
 |
|
 |
C6.7. The "gene gun" used for biolistic transformation of plants. The petri dish contains plant tissue or protoplasts.
|
|
C6.8. Transgenic papaya resistant to Papaya ringspot virus (PSRV) (Right) and susceptible papaya (Left). Plant embryos received the coat protein gene of PSRV by biolistic transformation. Genetically engineered papaya were developed in the United States and have been sold in this country since 1997. Approval to sell the papaya in Japan was received in 2010. |
|
|
|
 |
|
|
| C6.9. Wild carrot or Queen Anne's lace (Daucus carota) from which modern carrots were derived by breeding. Top, flowers. Bottom left, roots of wild carrot. Bottom right, cultivated carrots. |
|
|
| |
|
|
